HTTP Header FTS
All HTTP headers including requests (GET, POST,..etc) and responses (HTTP OK, errors ) are stored in the FTS index.
What is Stored ?
The entire HTTP request or response body is treated as a single document. All fields are stored in the index except the following which have high variability. You can generate reports by User-Agent, Server, Content-Type, or any of the fields in the HTTP Header.
Cookie, Set-Cookie, Date, Expires, Last-Modified,E-Tag, P3P, ETag, Cache-Control, Keep-Alive,Age,Last-Modified, If-, Location, Content-Length, Referer
The following extra attributes are added by Trisul to aid some kinds of useful queries
- CODE - HTTP response code
- URI - The full URL
Sample Document
A typical document looks like this
POST /ajax/ufi/like.php HTTP/1.1
Host: www.facebook.com
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Ubuntu; Linux i686; rv:11.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/11.0
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Language: en-us,en;q=0.5
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Connection: keep-alive
X-SVN-Rev: 810660
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8
Referer: http://www.facebook.com/
Content-Length: 368
Using
👉 Select Resources → HTTP Header FTS
Follow instructions in the FTS documentation.
Special Tips for HTTP Header FTS
Special Attributes
You should leverage the special attributes URI and CODE to narrow down your search.
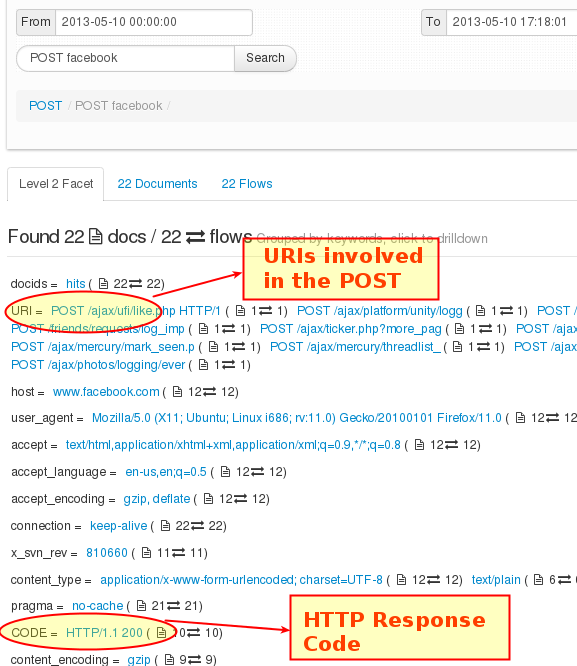
Figure: Showing URI and CODE attributes
Documents to Flows
Once you have sufficiently narrowed down your documents of interest.
- Switch to Flows
- Use the Options dropdown menu and the URLs in flow to switch to the URL normal index page.
- Use the Download PCAP button at the top to download all the flows shown at once
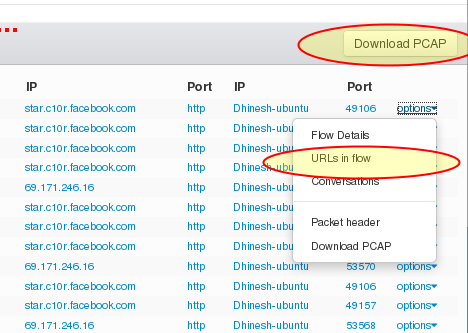
Figure: Click on options to bring up pivoting options to other kinds of data